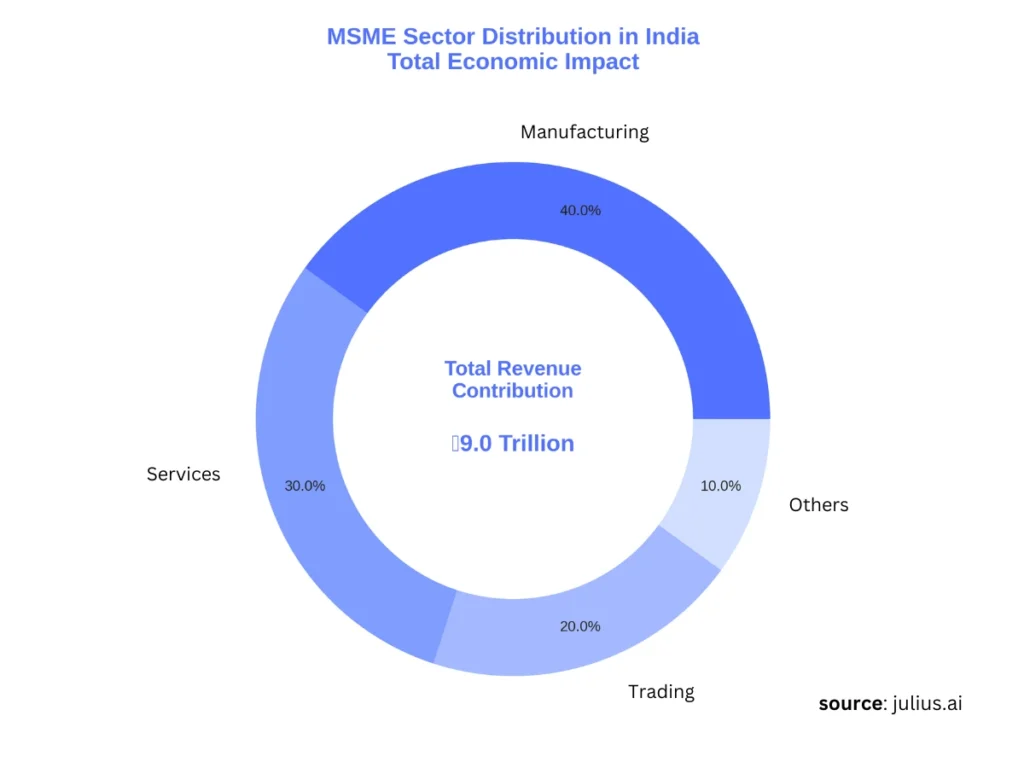
MSMEs are more than just small businesses; they are the backbone of India’s economy. They drive innovation, create jobs, and power the growth of communities across the country.
But what does this really mean? What constitutes an MSME, and why is it so important?
That’s what we’re trying to break down in this guide what MSMEs actually are, who can be considered an MSME, the benefits they provide, and what you need to know.
We promise: We keep it super simple and jargon-free. If you are an aspiring entrepreneur or just a curious person, this post will be helpful to you.
What is an MSME?
Let’s begin by understanding what qualifies a business as an MSME.
These aren’t just businesses that are small in name, but rather classification based on definite investment and annual turnover criteria.
And, once a business meets such criteria, opportunities open up from financial aid to market expansion support.
Here’s the breakdown:
Micro Enterprises: These are the smallest of the small. To be a micro-enterprise, your business needs to have:
Investment: Less than ₹1 crore.
Annual Turnover: Less than ₹5 crore.
Small Enterprises: These are a bit larger than micro-enterprises. To be considered a small enterprise, your business needs to have:
Investment: Less than ₹10 crore.
Annual Turnover: Less than ₹50 crore.
Medium Enterprises: These are the largest of the MSMEs. In order to be considered a medium enterprise, your business will have to undergo the following conditions:
Investment: Less than ₹50 crore.
Turnover: Less than ₹250 crore.
Important Note: It is not that you qualify either under the investment or turnover criterion; both have to be satisfied. Additionally, manufacturing or services, whoever they are does not matter because everyone falls within the same ambit.
Who Can Be an MSME?
The good news is that a wide variety of businesses can be MSMEs.
Here’s a look:
All kinds of industries: Manufacturing, services, wholesale, and retail all fall under the MSME umbrella, as long as they meet the investment and turnover criteria. The only exceptions for wholesale and retail are businesses dealing in motor vehicles and motorcycles.
Various business structures:
- Individuals, startups, and entrepreneurs
- Private and public limited companies
- Sole proprietorships
- Partnership firms, such as Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs)
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
- Co-operative societies
- Trusts
Student/Entrepreneurs: Student or entrepreneur from a variety of institutions including Technical colleges, universities, other professional colleges/institutes, R&D institutes, NGOs engaged in relevant activities, MSME-DIs/Technology Centers(TCs), DICs or any institute/organization of Central/State Govt.
Innovation-focused businesses: Any individual or MSME with innovative ideas ready for commercialization can go to IITs, NITs, technology institutes, and research institutes for collaboration.
Specific Manufacturing Businesses: Businesses involved in the production of khadi (cotton, silk, woollen) and polyvastra, or any manufacturing MSME that applies for the Lean Manufacturing Competitiveness scheme.
📘Also read: 51 MSME Business Ideas Across Growing Industries
The Udyam Registration or MSME Registration
The government of India has made it easier to get recognized through the process known as Udyam Registration, which is the registration process available online that aids one in getting the official identity for being an MSME.
Not compulsory, this is highly helpful because it lets you open lots of doors in the way of various government benefits.
What does it do: It is the easy way for you to get yourself registered as a micro, small, or medium enterprise.
How it works: It fetches your investment and turnover information automatically from the government database with the help of your PAN and GST.
Benefits: This registration is not compulsory, but you will enjoy benefits at the government level.
All types of entities, including individuals, startups, private and public limited companies, sole proprietorships, partnerships, Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), cooperative societies, and trusts, can register.
What Benefits Do MSMEs Get?
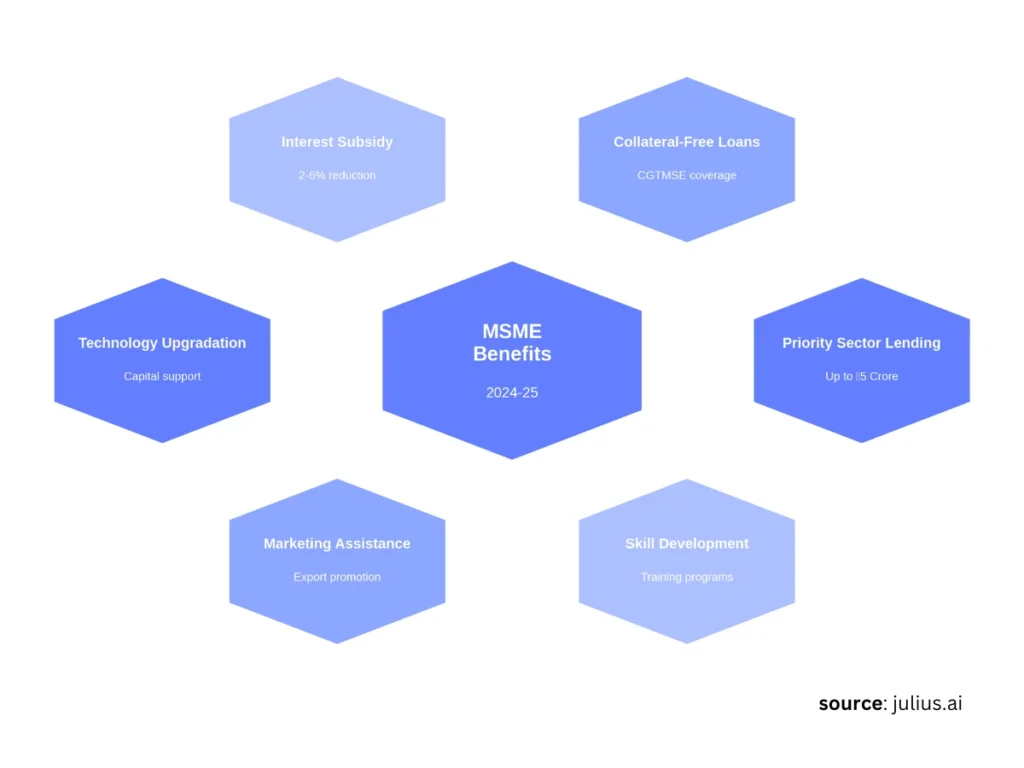
So, what are the perks of being an MSME?
The government has numerous ways to help these businesses grow and thrive. Here are just some of the benefits:
Financial Benefits
Credit Guarantee Scheme: They receive collateral-free loans up to ₹50 lakh through the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE).
Credit Linked Capital Subsidy (CLCS) for Technology Upgradation: Obtain a 15% upfront capital subsidy for adopting well-established and improved technologies.
Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP): Financial assistance for setting up new projects, with subsidies varying according to the area and category of the beneficiary.
Bank Credit Facilitation: NSIC will handle all the documentation to help you complete and submit your credit proposal to the banks.
Raw Material Support: NSIC may provide funds to purchase raw materials so that the MSME sector can focus on quality production.
Bill Discounting: Your bills arising from trade transactions are discounted with the aid of NSIC.
Working Capital Loans: There are many schemes which provide assistance for working capital to sustain operations.
Refinance for Textile Industry: Financial support to textile industries for modernization.
Marketing Support
Marketing Assistance: Get assistance for participation in international exhibitions, and trade fairs and for organizing buyer-seller meets.
Marketing Development Assistance (MDA): Funding to exhibit at overseas trade fairs and use Global Standards (GS1) in barcoding.
Single Point Registration Scheme (SPRS): Obtain registration with NSIC for involvement in government tenders and the EMD would not be payable.
Marketing Intelligence Cell: Have access to details about the buyer, exporter, and technology provider, all of which could assist your business.
Marketing Hubs: Support in setting up marketing hubs with funding.
Market Development Assistance (MDA): MDA is given by the KVIC, which distributes it to various stakeholders, such as spinners, weavers, and sales institutions.
Technology Upgradation
Technology and Quality Upgradation: Schemes to enable you to adopt energy-efficient technologies, reduce production costs and shift to clean development mechanisms.
Design Clinic Scheme: Schemes for acquiring solutions to design issues.
Lean Manufacturing Competitiveness Scheme: Grants to adopt lean manufacturing.
Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE): Financial and policy support to set up or strengthen technology incubation centers.
Common Facility Centers (CFCs): Schemes for the development of common facility centers for testing, training, raw material depots, and so on.
Training and Skill Development
Assistance to Training Institutions: All support – fund flow towards creation/ strengthening of infrastructures of training institutions, and entrepreneurship/skill development programs.
Human Resource Development: Programs for creating a nucleus of trained trainers.
Skill Development Programs: Programs that develop the skill level of workers.
Intellectual Property Rights Awareness
IPR Scheme: Financial support for the propagation of awareness programmes, pilot studies, and specific training in the area of IPR to protect business ideas.
Infrastructure Support
Exhibition Grounds: The ground is offered for display purposes by MSMEs.
IT Incubator: Pre-equipped built-up space with standard amenities for a new venture.
Specific Sector Schemes
Ministry of Textiles schemes: Assistance for the textiles industry in infrastructural and technological advancements
Ministry of Agriculture Schemes: Scheme related to horticulture, cold storage and other agricultural infrastructural facilities.
Ministry of Food Processing Industries schemes: Mega food parks, cold chains, etc., to promote food processing; various infrastructural aids for food processing.
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Schemes: Schemes concerning waste minimization and implementation of clean technologies.
AYUSH Ministry Schemes: Initiatives to promote the practice of Ayurveda and other traditional modes of healing.
Ministry of Mines: Scheme for the exploitation of construction material.
Ministry of New and Renewable Energy: Grants for R&D in the area of renewable energy.
Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region: Financing of industries located in the North Eastern region
Ministry of Social Justice Schemes: Welfare programs for scheduled castes and other weaker sections
Other Benefits
Tax incentives in the form of tax exemptions or rebates on various schemes for MSMEs.
Access to government tenders: MSMEs gain a competitive advantage in tendering for government contracts and may even enjoy preference and price advantages.
How to Apply for Schemes
The procedure for applying for each scheme will be different. However, here are a few general things to remember:
Online Applications: Most schemes ask you to apply online.
Prescribed Formats: You may have to fill up a particular application form.
Supporting Documents: Be sure to have all the documents you require, such as your business registration details, project proposals, and other information that may be needed.
Contact the Right Office or Agency : You will contact the right office or agency in charge for the scheme in question. Such may be an MSME-DI office, NSIC or any other similar agency.
Key Takeaways
Scheme-Wise Eligibility: You should specifically check the requirements of the scheme you are applying for as it may vary with different schemes.
Registration: Getting registered under the MSME tag is very much required for several government schemes.
Compliance: All government compliances need to be followed strictly in order to remain eligible.
Continuity in Operations: For most schemes, your business must have been continuously operating for at least a particular period.
No Defaults: The company should not be in default of any government scheme or financial institution.
References
Udyam Registration Portal For all entrepreneurs who are interested in getting their business registered as an MSME, the Udyam Registration Portal is vital
List of Host Institutions The individuals or MSMEs who have innovative ideas can approach the host institutions to seek support.
National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) Website NSIC offers several services and schemes to the MSME sector such as credit facilitation, raw material assistance, and marketing support.
Information of MSME Scheme To obtain details about the schemes including application forms and guidelines you can log in to the website
MSME Ministry Website Information regarding the schemes available with the MSME ministry.
Mudra Bank Website For details of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana, including nodal officers.